A characteristic feature of Psoriasis, the location of the papules is skin symmetrically on the extensor surfaces of the skin of the hands and the legs, as well as the head.

Despite the fact that plays a leading role in the development of Psoriasis, the availability of genetic predisposition (Psoriasis refers to diseases, sexually inherited), the impetus for the development of the disease can cause a variety of exo-and endogenous factors (development of Psoriasis in the nervous system, against the background of endocrine disorders, infections diseases, etc.).
Etiological factors in the development of the disease
The disease has no sexual orientation, so that the frequency of occurrence of Psoriasis in men and women is different. In 12 percent of patients, the disease develops for the first time to ten years. Twenty years before psoriasis develops in forty-six percent of the patients, and thirty years at sixty percent.
In the development of Psoriasis two age peaks:
- twenty-seven and fifty-four years for men;
- five, ten and fifty-four years for women.
Causes of Psoriasis in adults
The exact cause of Psoriasis is unknown. The leading role in the pathogenesis of the disease belongs to a genetic predisposition. Also, a significant role in the formation of the immunological instability, Lipid plays a herd of disorders, and the presence of the patient of chronic infection.
In favor of genetic theories (inherited causes of Psoriasis) is shown in the fact that the illness affects not only the patient, but also his close relatives.
Reveal predisposition to Psoriasis may be used in the implementation of the classical analysis of the genome. In these patients, there may be ten Loci of the chromosomes, the hereditary predisposition to a disease (PSORS 1 through 9, as well as HLA – B27, 17, etc.).
The most important gene, the faith for a maximum of pronounced congenital predisposition to the development of the disease, PSORS1.
Also in the pathogenesis of Psoriasis play an important role in genetic metabolic disorders of carbohydrates and lipids. In the majority of patients with Psoriasis severe hyperlipidemia and metabolic syndrome. In this regard, there is a high risk of developing severe early atherosclerotic lesions of the blood vessels and cardiovascular disease in patients with Psoriasis.
In addition to hyperlipidemia, to be celebrated in disturbed metabolism of LCD (fatty acids), the increased production of free radical compounds involved in the keratinization of the Epidermis, etc.
In the investigation of psoriatic Plaques, the large content of oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein.
The most important markers, assess the Proliferation of the keratinocytes in the outbreak of Psoriasis, the Protein Ki67, and Keratin-six, sixteen, and seventeen. These markers are responsible for the processes expressed in terms of hyperplasia, violation of differentiation of cells and development of inflammatory reactions in the dermis.
Because of this, even in the presence of the recovery stage in Psoriasis (disappearance of the inflammation of the Epidermis), saves the inflammatory process in the blood vessels of the Dermis.
Also in the development of inflammation in the onset of Psoriasis is a role of activated T-lymphocytic cells, mediators of inflammatory reactions, inflammation in the micro-vascular system of play. To identify in the investigation of the microflora of the skin in patients with Psoriasis and streptococci, provoke the development and exacerbation of Teardrop Psoriasis.
The immunological basis of the development of the pathogenesis of Psoriasis, the development of immune-competent cells, activated second-CD4+ T-lymphocytic cells and cytokines with anti-inflammatory effect. For this theory by the fact that the monoclonal antibody in Psoriasis, the anti-activated second-CD4+ T-lymphocytic cells, a significant therapeutic effect. Effective means against psoriasis is a drug for inhibiting the production of Tumor necrosis factors.
Contagious, whether the Psoriasis of the skin other
No. Psoriasis is a genetic disease.
Is transferred, whether the Psoriasis from person to person
No. Infected with Psoriasis from another Person is not possible. In spite of the fact that streptococcal infections trigger function factor can occur in people without a genetic predisposition for the development of the disease, psoriasis.
Is transferred, whether Psoriasis sexually
No. Psoriasis is not contagious and is not transmitted, no droplets in the air, no contact, neither sexually nor in any other way.
Is transmitted, if the psoriasis is inherited
For the development of Psoriasis, a genetic (hereditary) predisposition. Therefore, the disease is common in close relatives. In the presence of Psoriasis in the parents, there is a high risk for the occurrence of psoriasis, and in the case of a child.
However, some authors distinguish separately Psoriasis of the second type. It is assumed that this variant of psoriasis development in patients after forty years and affects mainly the joints and the nail plate, which is not related with inheritance.
Whether you die from psoriasis
No. Psoriasis is not life-threatening disease. The prognosis for life in such patients cheaper.
However, Psoriasis is considerably more difficult full life of the patient, brings him a lot of discomfort and lowers your social activity.
It should also be noted that the pustular forms of Psoriasis can be hard to lick extreme, accompanied by melt and festering pustules, with the further otpadeniem of the skin according to the type of "purulent lakes". In the process, perhaps the development of erythroderma, secondary bacterial complications, joint damage, etc. is
The triggering factors in the development of Psoriasis
Aggravating factors are the occurrence of exacerbation of Psoriasis,:
- Breach of the skin cover;
- endocrine disorders;
- Pregnancy;
- the emergence of metabolic disorders;
- the preparations of Beta-adrenoblokatorov, mi means-in etc.;
- the presence of foci of chronic infection (especially streptococcal infections);
- Alcohol abuse;
- Smoking;
- excessive exposure to the sun;
- captivating sharp, sweet, greasy foods, etc;
- acute infectious diseases;
- Exacerbation of allergic diseases;
- Stress, emotional overload (psoriasis in the nervous system, escalated, most of the time).
Classification of psoriasis
According to the varieties of forms of Psoriasis can be distinguished:
- vulgaris (common forms of Psoriasis);
- exudative;
- the outdated Palmar-plantar;
- warty;
- follicular;
- the nail;
- Pustule formation;
Over the course of the disease: Progressive, stationary character can wear.
On the prevalence of lesions mark limited, widely used and generalized.
Also there may be a seasonality of exacerbations: Winter, summer, and indeterminate (not associated with the season of the year) exacerbation of Psoriasis.
Photo, symptoms and treatment of Psoriasis in adults
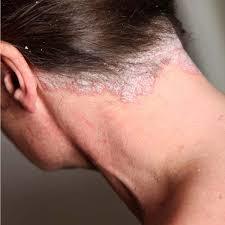
For psoriasis is characterized by the appearance of pink-reddish or bright red papules, covered with silvery, white scales covered in a loose consistency. Itching of the skin may be missing. Many patients notice the feeling of tightness of the skin.
Intense itching is characteristic, in General, for Psoriasis-skin lesions of the scalp and the perineum.
The occurrence of pain in the joints is in the development of psoriatic Arthritis.
The most characteristic Manifestation of Psoriasis is the triad of specific symptoms :
- the emergence of the phenomenon Stearin spot (reinforcement Peeling in the diagnosis of Psoriasis papules, which is like a drop of Stearin);
- the formation of the terminal movie (appearance, ultra-thin, transparent film, genocide, after, when poskablivanii all desquamation) to be separated;
- the formation of blood Tau, or the presence of punctate bleeding at the site of the rejection Terminal-films.
Psoriatic papules isolated character can wear, or merge. Size can vary from fine to the big surface of the skin. The most common localization of the lesions are the elbows, knees, and head (your fibrous part) and the lower back.
In rare cases, Plaques in the mucous membranes of the cave, lips and mouth can affect.
In children, elderly patients and patients with Diabetes mellitus, can develop plicata Form of the disease. In this case, the skin appears behind the ears, armpits, Perineum, gluteal folds, the navel, and under the mammary glands.
In patients with Psoriasis as peeling may be missing. The surface of the psoriatic lesions can be absolutely smooth, bright red. In some cases, it is possible that the appearance of the maceration wrinkles.
In some patients the only Manifestation of the disease, Plaques on skin and mucosa can be of the sexual organs to the skin.
In General, psoriatic skin lesions to bear the symmetrical nature, however, can be observed in some patients, unilateral rashes. It is the appearance of the curly psoriatic lesions (annular, arcuate, geographical, etc.) is also possible.
In patients with continuous-occurring disease, long-existing Plaques on the skin of the lumbar and gluteal region can be accompanied by with the advent of the warty growths.
In addition, the causes of the warty forms of Psoriasis can be used:
- purulent infections of the skin;
- wrong external treatment (usually self-medication);
- overweight.
In the case of warty forms of the disease, the scales begin to stick to each other and formed on the surface of platelet-yellow crusts.
In some patients in Isolation to the expiration of Palmar-plantar Psoriasis may also occur. In this case, the Patient will interfere with painful cracks, pustules, papules, erythematous-squamous Plaques on the palms and soles of the feet.
Frequent Manifestation of Psoriasis the defeat of nail plates. In most cases, the formation of localised depressions on the surface of the nail (dystrophy). Also, deformation of the nail, longitudinal and transverse furrows, thickening of the nail plate, change the easing and color bleeding appear under the nail plate.
In psoriatic erythroderma, developing, usually on the background of excessive exposure to the sun or incorrect external therapy, appears to be a pronounced swelling of the skin, redness, intense itching and desquamation, fever, weakness, appetite. In the case of serious, perhaps, is the emergence of anemia, heart failure, and diseases of the kidney and the liver, dehydration, Alopecia areata appears.
Psoriasis and pregnancy – the threat to the child, characteristics
Psoriasis does not interfere with the reproductive ability, and is not a contraindication to pregnancy. It should be noted that in many women during pregnancy, the disease is more easily than usual. But about twenty percent of the women there may be a pronounced exacerbation of the disease.
Overall, the Psoriasis is not difficult, the course of pregnancy and the life of the child is not at risk. However, in patients with Arthritis, by increasing the load on the joints, there may be a significant deterioration. In generalized forms pustules Psoriasis, the occurrence of secondary bacterial complications.
It should be noted that since Psoriasis is not infectious refers to diseases that the mother may pass freely with the child and feeding him. The probability of the development of Psoriasis in a child in the future is about 15-20%, if one parent is ill and approximately 50% when both parents are sick.
The biggest difficulty of psoriasis in pregnant women is that it is contraindicated the most prescribed medications. Therefore, when planning pregnancy, you should at an early stage to your doctor, to correct in advance of treatment.
Self-treatment is strictly prohibited and can lead to considerable damage for both mother and child (some drugs have a toxic effect on the fetus).
The diagnosis of the disease
The diagnosis is made on the basis of the specific symptoms of (psoriatic triad). And also, if necessary, data of histological, immunological, and radiological examinations.

























