Psoriasis, or psoriasis, is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the skin and manifests as red patches, plaques covered with small scales. The disease is incurable, so treatments for psoriasis are limited to controlling symptoms, stopping pain and inflammation, and achieving early and long-term remission. There are many prejudices against the disease in society. People who don't know what it is believe that psoriasis can be transmitted. In the description, several types of this non-communicable disease can be distinguished, each with their own individual symptoms and progression.
Where does psoriasis come from?
The causes of psoriasis are not clear, as little is known about this skin disease. The symptoms of the disease in the initial stages can resemble dermatitis, eczema, but it is impossible to confuse pronounced plaques of psoriasis with other skin diseases. Scientists and doctors agree that one of the factors why psoriasis occurs is a genetic predisposition.
For example, if a mother is diagnosed with a skin condition, there is a 15% chance that the child will inherit the condition. If both parents are treated for psoriasis, the risk of hereditary transmission of the disease increases 4 times, that is, to 60%.
But even if the parents are carriers of a gene that causes a skin disease, it does not mean that the child will get sick. The causes of psoriasis on the body are different. Stress, nervous shocks, psychological trauma "trigger" skin diseases.
Psoriasis is also due to:
- Skin injuries, burns, insect bites, tattoos;
- medications the person is taking;
- infectious diseases;
- alcohol abuse, smoking;
- exposure to chemicals such as cleaning agents;
- dermatitis and fungal diseases;
- HIV;
- pregnancy and childbirth.
Recently, scientists have established that psoriasis can occur due to malnutrition, but no convincing evidence for this theory has been found.
Doctors know that a specific gene is responsible for the skin condition but cannot pinpoint the exact causes of psoriasis.
What does psoriasis look like in the early stages?
The first symptoms of psoriasis look like this:
- A person's nails peel and the skin cracks.
- A pustular rash appears on the body.
- The skin begins to peel off and die.
- There are blisters on the hands and soles of the feet.
- Itchy red patches covered with whitish scales appear on the elbows, knees, and face.
A person sinks into depression, not interested in anything, notices a breakdown and even low self-esteem.
On the head, face and under the hair
First of all, a person notices increased desquamation of the skin, resembling scales. Then plaques themselves appear, covered with silvery scales. The rash grows, affects more and more areas of the skin, but even with severe psoriasis, the hair does not fall out.
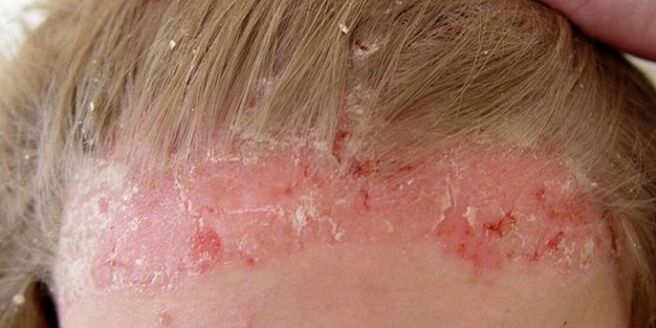
In 80% of cases, psoriasis mainly affects the scalp. If the pathology is not treated, rashes appear in other places.
A harbinger of a disease affecting the skin of the face is severe itching. At first, psoriasis resembles an allergy, the skin becomes covered with small red spots that increase in size and merge into an inflamed nodule or papule.
Eruptions cover the entire face. The spots themselves are covered with scales, which can be easily and painlessly separated. Underneath is a final film reminiscent of scarlet shiny leather. When combing itchy spots, they are covered with small drops of blood.
On arms and legs
Skin disease Psoriasis affects the skin:
- upper arms and legs;
- To brush;
- knuckles on hands and feet;
- near the nails.
The disease begins with the appearance of small reddened areas of a rounded shape on the skin between the fingers, on the shins, wrists, elbows and knees.
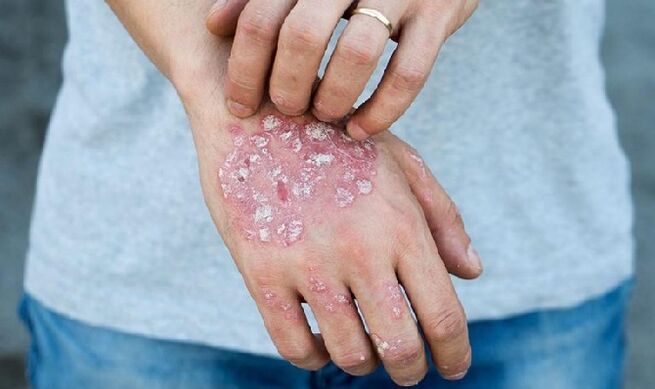
In 10% of cases, psoriasis affects the nails. Psoriasis plaques appear on the nail plates long before the main symptoms of the disease that affect the skin of the body appear.
On palms and feet
Palmar-plantar is called the manifestation of psoriasis affecting the skin of the palms and feet.
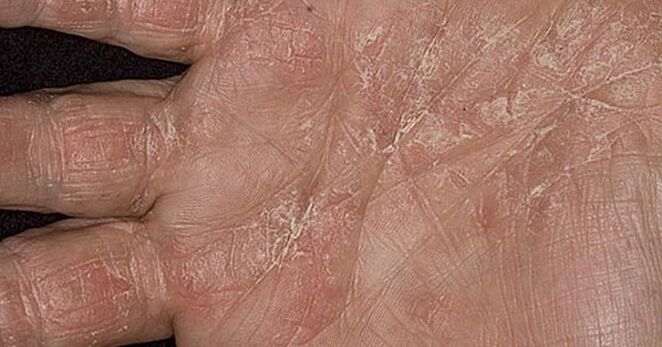
It is characterized by the appearance of red scaly spots covered with whitish scales. At the site of the rash, the skin thickens, cracks, and becomes inflamed. The aggravated form is manifested by the formation of pustules, deep abscesses.
On the torso
Signs of a disease affecting the skin of the body resemble psoriasis on the palms and feet, head and face. Rashes often appear on the back and lower back.
Red spots covered with grayish-white scales itch and itch. They cannot be combed, since the thin final film does not protect the smallest capillaries, and when combing, the surface of the skin is covered with microscopic blood droplets. Psoriasis can appear on the chest and sides.
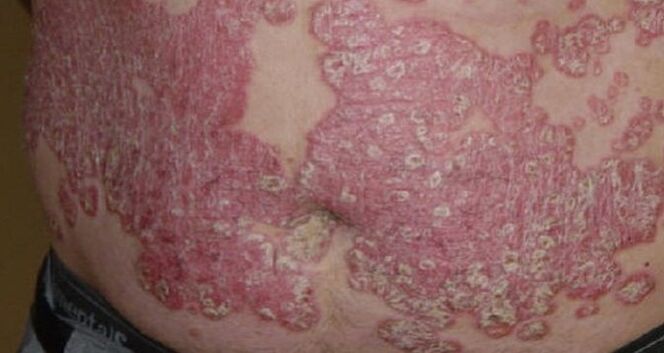
Red spots expand and merge into formations that doctors call "paraffin lakes. "
Psoriasis causes various skin changes:
- Peeling;
- Thickening;
- Edema;
- the appearance of blister-pustules.
Dry skin often cracks, causing pain and discomfort.
Other localizations
Psoriasis spreads throughout the body when the disease is ongoing. Psoriasis plaques can be localized in the groin, buttocks, elbow and knee creases. The disease causes great discomfort, because the rashes itch, but they should not be scratched. Careless action can easily damage the thinned affected skin and cause additional infection.
Symptoms of skin psoriasis are similar regardless of location, so a dermatologist diagnoses the disease as follows:
- red rashes with a clear border;
- the so-called psoriasis triad: the phenomenon of the "stearin spot", that is, the plaque itself, covered with silvery soft scales, the presence of a terminal film underneath and tiny droplets of blood covering the spot if it is scraped;
- the appearance of new plaques at the site of skin injuries;
- Itching.
psoriatic arthritis
This form of complication affects the joints, tendons, which lose their density and elasticity.
Arthritis accompanies the symptoms of psoriasis, is characterized by inflammation of the joints and is divided into:
- Asymmetric, affecting multiple joints on one side of the body and not affecting paired bone elements.
- Symmetrical, which resembles rheumatism. Paired joints suffer. This form often leads to disability.
- Interphalangeal distal joints affecting the phalanges of the fingers and toes.
- Spine, in one or more departments.
- Deformation when the joints are destroyed.
Inflammation of the joints is characterized by severe pain, swelling, the skin on the site of the affected bone joint has a bluish color. In this case, a person has a breakdown, sometimes the lymph nodes increase.
Classification of psoriasis
Types of psoriasis differ depending on the type of rash. The international classification describes 10 forms of a chronic autoimmune disease:
- The most common is plaque-like or simple psoriasis. It affects every part of the body, occurs in both women and men. It begins with the appearance of red, swollen patches, which are subsequently covered with a whitish, easily shed film of scales called "plaque".
- After a streptococcal infection, guttate psoriasis can affect the skin. It manifests itself in the thighs, lower legs, and also affects the neck and back. Rashes of red, bluish, lilac color rise above the surface of the skin and resemble drops in shape.
- The spotted form is characterized by widespread rashes all over the body. The disease occurs more often in women than in men.
- Pustule, the most severe, characterized by the appearance of blisters - pustules surrounded by red, inflamed skin and filled with clear fluid. If an infection gets into the blisters, fragments of pus appear in the contents.
- Follicular, affecting the skin on the legs and thighs in the form of small whitish papules.
- Psoriasis of the flexor surfaces, which affects the skin in the folds, for example in the knee creases, in the groin, under the breasts, armpits.
- Palmar-plantar, which often occurs in people who do physical work.
- Psoriatic onychia only affects fingernails and toenails. The nail plates change color, become yellowish, peel off, sometimes die. The skin around the nails thickens.
- The scalp, which is characterized by red scaly rashes in the area of hair growth and itching.
- Seborrheic, most often localized on the chest, behind the ears, between the shoulder blades, in the nasolabial folds. Psoriasis foci are strongly scaly, often similar to eczema, covered with purulent crusts.
- Symptoms of the erythrodermic form of psoriasis are pronounced. Affected skin can come off with plaques, a person experiences severe pain, body temperature rises. Untreated erythroderma flows into pyoderma - a purulent lesion of the skin - and can lead to death.
Any form of psoriasis requires timely treatment, which can only be prescribed by a dermatologist after examination and necessary examinations.
How psoriasis manifests itself at different stages
A total of 4 phases of the development of psoriasis are distinguished:
- initial or early;
- progressive;
- stationary;
- regressive.
In most cases, psoriasis begins with the appearance of small papules. Round, pink, shiny spots, sometimes no larger than a pinhead, rise above the skin's surface and have a clear border. They are covered with silver scales. The presence of rashes in the initial stages of psoriasis can be confused with eczema or an allergic rash.

The clinical picture of the disease at different stages varies. For example, severe inflammation of the skin is characteristic of an acute or progressive form that requires medical attention and intensive treatment.
However, the rashes do not disappear, but increase and merge with each other. Psoriasis plaques, clearly delimited by a pink corolla, begin to shed. The affected skin itches and itches unbearably.
It lasts from 2 weeks to several months, and psoriasis goes into a stationary stage. The growth of psoriatic plaques stops, the peeling increases and covers the entire affected area of \u200b\u200bthe skin.
With regressive psoriasis, peeling gradually disappears, psoriatic plaques flatten and gradually disappear. There are no marks, scars or scars on the skin. Sometimes there is hyperpigmentation of the skin. In the remission stage, the skin takes on a normal color and texture.
What is the danger of the disease
The severity of the course of the disease depends on the condition of the skin. If the lesions are not extensive, the person leads a normal life. Physical and psychological discomfort is felt by people whose rashes occupy a large area, the skin becomes inflamed. A significant health risk is a complication of pustular psoriasis when infection has penetrated the vesicles.
Psoriatic arthritis is also dangerous because some of its forms destroy the joints and lead to disability. However, inflammation of the bone joints develops very rarely, in 10% of cases.
Even if the plaques on the skin are insignificant and the person feels normal, it is necessary to undergo an examination by a dermatologist, who will make a diagnosis and begin treatment. Timely access to a doctor will prevent complications and contribute to stable remission.
Complex treatment of psoriasis
There is no effective way to get rid of psoriasis forever. Skin diseases are treated with various means. A person is prescribed pills, ointments and physical therapy. It is recommended to take healing baths and pay careful attention to the condition of the skin to avoid injuries such as scratches, cuts and scratches.
Comprehensive treatment for psoriasis works when a person follows doctor's prescriptions.
How is psoriasis treated with pharmaceutical products?
These are ointments, tablets, and injections that the attending physician prescribes to the person seeking help. Tablets are drunk at the appointed time of the day before or after meals, ointments are applied to the affected areas with clean hands, injections can be done at home or in the hospital. These can be products based on plant components, hormones and other chemically active substances.
In the complex therapy of scaly lichen use:
- Antihistamines, which are prescribed when a person develops an allergy.
- Hepatoprotectors that support the liver.
- Immunomodulators that facilitate the course of the disease.
- Immunosuppressants in the form of injections. They are effective but expensive and have serious side effects. The drugs should not be used by people with infections or oncology.
- Glucosteroids are effective but addictive. Therefore, treatment with hormonal drugs lasts no more than 2 weeks.
When psoriasis is mild, doctors try to limit themselves to topical medications.
Medicines for topical use - ointments, sprays
Local remedies for psoriasis are divided into:
- Hormonals that affect the body's autoimmune processes.
- Therapeutic, including zinc, naftalan, tar, vitamins. They moisturize cracked skin, soften hardened psoriasis lesions, support skin function and restore damaged layers.
Hormonal ointments, lotions and sprays for the skin are used during an exacerbation. Bioactive substances in the composition of potent creams:
- reduce itching;
- relieve swelling;
- narrow blood vessels;
- Relieve pain and fight inflammation.
Apply the product to the affected areas of the skin on the body, face and head. Medicinal ointments are most often used after the acute phase of psoriasis passes, and doctors recommend using hormonal preparations and creams with vitamin D for no more than 2 weeks.
pills and injections
A person interested in the treatment of psoriasis can ask a dermatologist about effective pills and injections used in complex therapy of psoriasis.
- For severe psoriasis, some medications are prescribed. For example, pills that a person receives when damaged skin does not heal.
- The doctor prescribes B vitamins, folate, omega acids, other multivitamins, and lecithin. These drugs help recovery, do not cause addiction, reduce the duration of treatment and prolong remission.
The complex therapy of psoriasis is not limited to taking special active substances and vitamins.

If a person follows the rules, uses high-quality cosmetics, maintains health and the condition of the skin, then psoriasis is practically not bad for him.
If there are no contraindications, a person can give injections with immunosuppressive drugs:
- Some drugs are given subcutaneously, while others are given intravenously to treat psoriatic arthritis.
- Injections have serious contraindications. They can not be used by people under 18 years old, pregnant and breastfeeding people, in the presence of malignant tumors and infectious diseases.
homeopathy
Manufacturers of homeopathic remedies claim that the use of such medicines reduces the risk of recurrence and guarantees a speedy recovery from the problem. Additional means:
- Support immunity and internal organ health.
- They are a source of minerals and vitamins that the body needs.
- Restore the work of the intestines and seed the digestive tract with beneficial bacteria.
- Helps eliminate toxins.
When choosing medicines, the homeopath takes into account the history, stage and nature of the course of the disease, heredity and the psychosomatic factor.
Official medicine has no evidence of the effectiveness of homeopathic remedies in the treatment of psoriasis.
Physiotherapy in the fight against skin diseases
Most often, the affected skin is irradiated with light waves of the ultraviolet spectrum of different lengths or with a laser. Sometimes, before the procedure, a person takes psoralens, which increase the sensitivity of skin cells to radiation. The doctor also prescribes cryotherapy if the affected skin is exposed to low temperatures. More recently, ultraviolet blood irradiation has been used to treat psoriasis.

UV irradiation is one of the simplest methods of physiotherapeutic treatment. At the same time, the effectiveness of this method showed quite convincing results.
Sessions vary in length, but physiotherapy is very effective. This is a way to quickly cure psoriasis. Procedures return activity to a person, allowing him to live and work fully.
Is it possible to cure psoriasis forever folk remedies
Psoriasis is not treatable. Tablets, ointments, injections fight the symptoms of the disease and reduce the number of relapses. Folk remedies are no exception. Decoctions, tinctures, medicinal baths contribute to the onset of remission, but do not relieve the autoimmune disease.
Drugs for oral administration
Means based on medicinal herbs and plants will help stop the symptoms of psoriasis. The safest are chamomile decoction, fresh aloe juice, compresses and decoctions of rhizome and burdock leaves.
In pharmacies you can buy herbal preparations for psoriasis. They can be brewed with boiling water, infused and drunk before or after a meal, or you can pour it into water and take therapeutic baths.
According to traditional medicine, the use of hydrogen peroxide eliminates the manifestations of psoriasis. Use the drug:
- In the form of a solution. First, dilute one drop of the product in 3 tablespoons of water and drink on an empty stomach half an hour before meals. Gradually increase the strength of the solution to 10 drops for the same amount of water. Take the medicine every three days.
- Externally, compresses are applied to the affected skin for an hour, wetting sterile gauze in a solution of 2 teaspoons of peroxide and 50 ml of water.
Before using any folk remedy, consult your doctor.
compresses and baths
Compresses and baths with decoctions of medicinal plants do not cure the disease, but they relieve the general condition, relieve itching and inflammation. Brewed for external use:
- Chamomile;
- succession;
- Thyme;
- burdock root;
- oak bark;
- jump;
- sage and others.
It is not recommended to take baths longer than 20 minutes.

After bathing, moisturizing creams and therapeutic ointments are applied to the skin.
Baths and compresses with herbal decoctions have practically no contraindications.
Skin protection and care
There is no complete cure for psoriasis. But throughout the period of treatment and during the period of remission, a person needs to properly care for the skin:
- Avoid traumatic effects on the skin. Don't scratch, don't scratch. Use protective equipment when doing physical work or cleaning.
- Wear comfortable clothing made from natural materials.
- Use special dermatological cosmetics.
- Moisturize the skin.
- Avoid direct sunlight.
Preventive measures also include the diet and lifestyle changes that the person makes.
change lifestyle and diet
Food is not the cause of psoriasis, but malnutrition weakens the body's defenses and reduces resistance to stressors. Therefore, a person with scaly lichen needs to monitor the daily routine and diet.
If the doctor is asked how to treat psoriasis, he will list preventive measures:
- Refusal of heavy, fried, greasy food.
- Active lifestyle, moderate physical activity.
- Sunbathing in the evening and morning hours.
- Quit smoking and alcoholic beverages.
A person should give preference to healthy meals with a high content of nutrients, vitamins and minerals.
What to do if a child is sick?
The first thing parents do, noticing the manifestations of scaly lichen on the skin of children, is to consult a doctor. Treating the disease in the early stages can reduce the intensity of the rashes that cause physical and emotional distress in children.
It is necessary to teach the child to properly care for the skin and follow a healthy lifestyle. Socialization is very important for children, so parents should encourage the child's desire to play sports, make friends, attend circles. To cope with emotional discomfort, children may need the help of a psychotherapist, who can teach them not to respond to possible silly remarks from their peers and even narrow-minded adults.
Is Psoriasis Completely Curable?
A person, faced with itchy, scaly rashes that bring physical and psychological discomfort, tries to find out whether this disease is treated or not.
You can learn all about psoriasis and its treatment from your dermatologist, whom you consult. There are associations and advice centers where you can also get the necessary information, including legal information, for example what services are due when you are diagnosed with psoriasis.
It is impossible to completely cure psoriasis, since the disease is associated with a gene factor, and genes are not amenable to drug therapy, procedures, homeopathy and folk remedies.
Modern drugs, ointments and procedures really effectively fight the symptoms of the disease and prolong remission. But regardless of the methods used, psoriasis can return. The disease occurs more often when a person neglects medical examinations and does not follow simple rules of prevention.
Can the disease be prevented?
"Three pillars" on which the prevention of skin diseases is based:
- Compliance with the rules of personal hygiene.
- Proper nutritious diet.
- rejection of bad habits.
For washing it is better to use only cosmetic dermatological products purchased at a pharmacy. Well, if they contain tar.

























